It’s now more important than ever for retailers to create a seamless and engaging retail customer journey across physical stores and digital channels. Retailers need to understand how customers interact with their brand at every stage of their journey, from the moment they first learn about the brand to their engagement after making a purchase. Creating a retail customer journey map is one of the most effective ways to achieve this understanding. A retail customer journey map can help visualize and optimize customer experiences, improving satisfaction and retention and, ultimately, drive sales.
In this article, we’ll explain what a customer journey map is, its relevance to retail, and why it is essential for modern businesses. Additionally, we will offer insights on how to create a journey map for omnichannel customers, focusing on, personas, stages, and touchpoints. We will also provide a framework that you can use to develop your own map.
What is a retail customer journey map?
A retail customer journey map is a visual representation of the steps a customer takes when interacting with a brand. It outlines every touchpoint, from initial awareness through to purchase and beyond, into post-purchase support and loyalty. In the retail sector, this could include interactions like visiting a physical store, browsing online, or engaging with social media. The journey map helps you understand these interactions from the customer’s perspective, highlighting pain points and opportunities for improvement.
By documenting each phase of the customer’s journey, you can better anticipate customer needs and expectations. This leads to more informed decisions about optimizing interactions, whether it’s ensuring good service at a checkout counter or personalizing follow-up emails after an online purchase.
What is a customer journey map used for?
Retail customer journey maps serve multiple purposes. Primarily, they help businesses understand how customers interact with their brand across different channels and touchpoints. By analyzing this data, you can create strategies to improve customer engagement, making the shopping experience more enjoyable and efficient.
Journey maps are also important for identifying bottlenecks in the purchasing process, such as difficulties navigating a website or long checkout lines in-store. With this insight, you can take specific steps to improve the retail customer journey and remove obstacles that may lead to customer dissatisfaction or lost sales.
Why are customer journey maps important?
Retail customer journey maps are important because they offer a detailed look at the customer experience. With a visual representation of the journey, you can pinpoint exactly where customers face challenges, lose interest, or encounter friction. This insight is important for delivering a good experience across multiple channels, ensuring that customers have positive interactions no matter how they engage— in-store, online, or via social media.
Journey maps are particularly valuable in retail because they help businesses create more personalized experiences, which can lead to increased loyalty and repeat business. Additionally, understanding customer pain points allows you to proactively address issues, enhancing customer service and boosting satisfaction.
Omnichannel retail customer journey
Customers interact with brands across various platforms and devices, all of which affect their purchasing decisions. The omnichannel retail customer journey combines physical and digital channels to provide a seamless shopping experience. For example, a customer might start browsing on their smartphone, visit a store to see the product in person, and then complete their purchase on a desktop computer. It’s essential for this process—from the initial touchpoint to the final purchase—to be as integrated as possible to facilitate a smooth experience and ensure a successful sale.
By understanding the omnichannel journey, you can ensure that each platform—whether it’s social media, an e-commerce site, or a brick-and-mortar store—offers a consistent experience. This level of integration is important for building trust and loyalty among customers.
Example of a retailer customer journey
Let’s explore a retail customer journey through the lens of Apple and the purchase of a Mac computer. Imagine a customer using a different laptop for several years but considering purchasing a Mac. Their journey begins online, where they visit the Apple website to explore the latest MacBook models, comparing features, specifications, and price points. The sleek design, powerful processor, and glowing customer reviews spark their interest. They also watch review videos and unboxing tutorials to get a real-world sense of the Mac’s performance.
Still undecided, the customer heads to a nearby Apple Store for a hands-on experience. There, they can test the models on display, comparing screen clarity, speed, and weight. They engage with Apple’s knowledgeable staff, who provide in-depth answers about the Mac’s capabilities, software ecosystem, and long-term reliability. This in-store interaction helps solidify the customer’s choice.
After making their purchase in-store, Apple doesn’t stop at the sale. The customer receives an email with setup guides, tips on getting the most out of their new Mac, and recommendations for Apple accessories like Magic Mouse or a protective case. The experience continues with personalized support through AppleCare, ensuring they feel supported in their investment long after leaving the store.
This example showcases how Apple seamlessly integrates online research, in-store experience, and post-purchase engagement. By offering consistent touchpoints across digital and physical channels, Apple ensures the customer feels guided, supported, and satisfied at every step.
What should a retail customer journey map include?
A well-designed retail customer journey map should include several key components:
- Customer personas – represent different segments of your audience.
- Stages of the journey – including awareness, research, consideration, purchase, and post-purchase support.
- Customer touchpoints – such as website visits, in-store interactions, and customer service inquiries.
- Customer thoughts, feelings and pain points – analysis of customer emotions at each stage to identify areas for improvement.
Retail customer personas
Retail customer personas are fictional representations of your ideal customers, crafted from real data about your target audience. Creating these personas helps you understand the different types of customers interacting with your brand, enabling you to tailor the retail customer journey to meet their specific needs.
To gain a clear understanding of your customer personas, you should conduct market research on your customer base, utilizing both qualitative and quantitative feedback methods. This process will help you identify the unique personas relevant to your market. To help you get started, here are some common types of retail customer personas:
- The ‘Deal Seeker’ – motivated by discounts, sales, and promotions. They are price-sensitive and spend time comparing prices and looking for the best value.
- The ‘Brand Loyalist ‘– has a deep connection with your brand and regularly makes repeat purchases. Their journey often starts with your loyalty programs and they engage with your content across multiple channels.
- The ‘Convenience Shopper’ – prioritizes speed and ease of shopping, focusing on getting what they need quickly through fast delivery or in-store pickup.
- The ‘Product Researcher’ – detail-oriented and thoroughly investigates product features, reviews, and comparisons before making a purchase.
- The ‘Impulse Buyer’ – driven by emotions or spur-of-the-moment decisions, often sparked by eye-catching product displays, limited-time offers, or targeted ads.
Retail customer journey stages
Mapping the retail customer journey involves breaking down the stages a customer goes through from the moment they become aware of your brand to post-purchase activities. Understanding these stages allows you to enhance customer satisfaction at each step, improving the overall experience. Here are the key stages of a retail customer journey:
- Awareness – the customer first becomes aware of your brand or product through ads, social media, word-of-mouth, or window displays. The goal is to grab attention and create a lasting first impression.
- Consideration – customers compare your products with competitors, read reviews, and seek out detailed product information. Providing clear, compelling information that showcases your value proposition is critical here.
- Purchase – the customer decides to make a purchase, whether in-store or online. This stage should offer a seamless and convenient transaction process with multiple payment options and transparent pricing.
- Post-Purchase Support – ongoing support through follow-up emails, warranties, customer service, and easy return policies ensures customers feel valued and confident in their decision.
- Loyalty and retention – Building long-term customer loyalty through personalized offers, loyalty programs, and communication encourages repeat purchases. Satisfied customers may become brand advocates, promoting your products to friends and family.
Customer journey touchpoints in retail
Retail customer journeys involve numerous interactions across various channels. Here are some of the most common touchpoints:
- Website – many customers’ first stop is your website. It needs to offer clear product information, easy navigation, and a smooth shopping experience to convert visitors into buyers.
- Social media – platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and Twitter provide opportunities for product discovery, engagement, and customer interaction. Social proof, such as reviews and testimonials, often influences purchasing decisions.
- In-store experience – physical stores allow customers to see, touch, and try products. Friendly, knowledgeable staff and a well-organized layout can greatly enhance customer satisfaction.
- Mobile app – retail apps provide a more personalized shopping experience, offering features like push notifications, exclusive offers, and easy access to past purchases or wishlists.
- Email marketing – a critical touchpoint for maintaining ongoing engagement, delivering personalized offers, product recommendations, and updates on sales or order statuses.
- Customer service – whether online chat, phone support, or in-store assistance, prompt and effective customer service can solve issues and ensure a smooth customer journey.
- Online reviews – Customers often check reviews before making purchasing decisions. Positive feedback builds trust, while addressing negative reviews demonstrates your brand’s commitment to improvement.
- Post-purchase communication – follow-up emails with order confirmations, shipping updates, or tips for product care help maintain a connection with the customer after their purchase.
- Returns and exchanges – A simple, customer-friendly return process adds to a positive customer experience, making people feel secure in their purchasing decision.
- Loyalty programs – Engaging customers with rewards, points, or exclusive offers encourages repeat purchases and deepens brand loyalty.
Customer thoughts and feelings
Throughout the retail customer journey, thoughts and feelings play a significant role in shaping how customers perceive and interact with a brand. Initially, customers may feel curiosity or excitement when discovering a product, followed by cautious optimism as they research and compare options. They may experience anticipation or anxiety during the purchase process, especially if the checkout or delivery process is unclear or complicated. Positive emotions like satisfaction or joy arise when expectations are met, but frustration, disappointment, or regret can surface if there are product, service, or support issues. Understanding these emotional responses is key for creating a journey that fosters positive feelings and long-lasting customer relationships.
Retail customer pain points
Retail customer pain points refer to the frustrations or obstacles that shoppers encounter throughout their journey, which can negatively impact their overall experience. These issues may include unclear product information, complex or lengthy checkout processes, inconsistent pricing across channels, and poor customer service or post-purchase support. Customers may also experience difficulties when returning products or accessing loyalty rewards. These pain points can cause dissatisfaction, reduce trust in the brand, and lead to cart abandonment or negative reviews, making it important to address and resolve them to improve customer retention and satisfaction.
How to visualize the customer journey
Creating a visual representation of the retail customer journey is a powerful way to understand the shopping experience. A well-designed visual map should include customer personas, stages of the journey, and touchpoints. By using a visualization, you can see the big picture and pinpoint areas where the customer experience can be improved. We have created an example of a retail customer journey map for the ‘Deal Seeker’ persona described above, mapping out the stages of the journey, touchpoints, and customer sentiment:
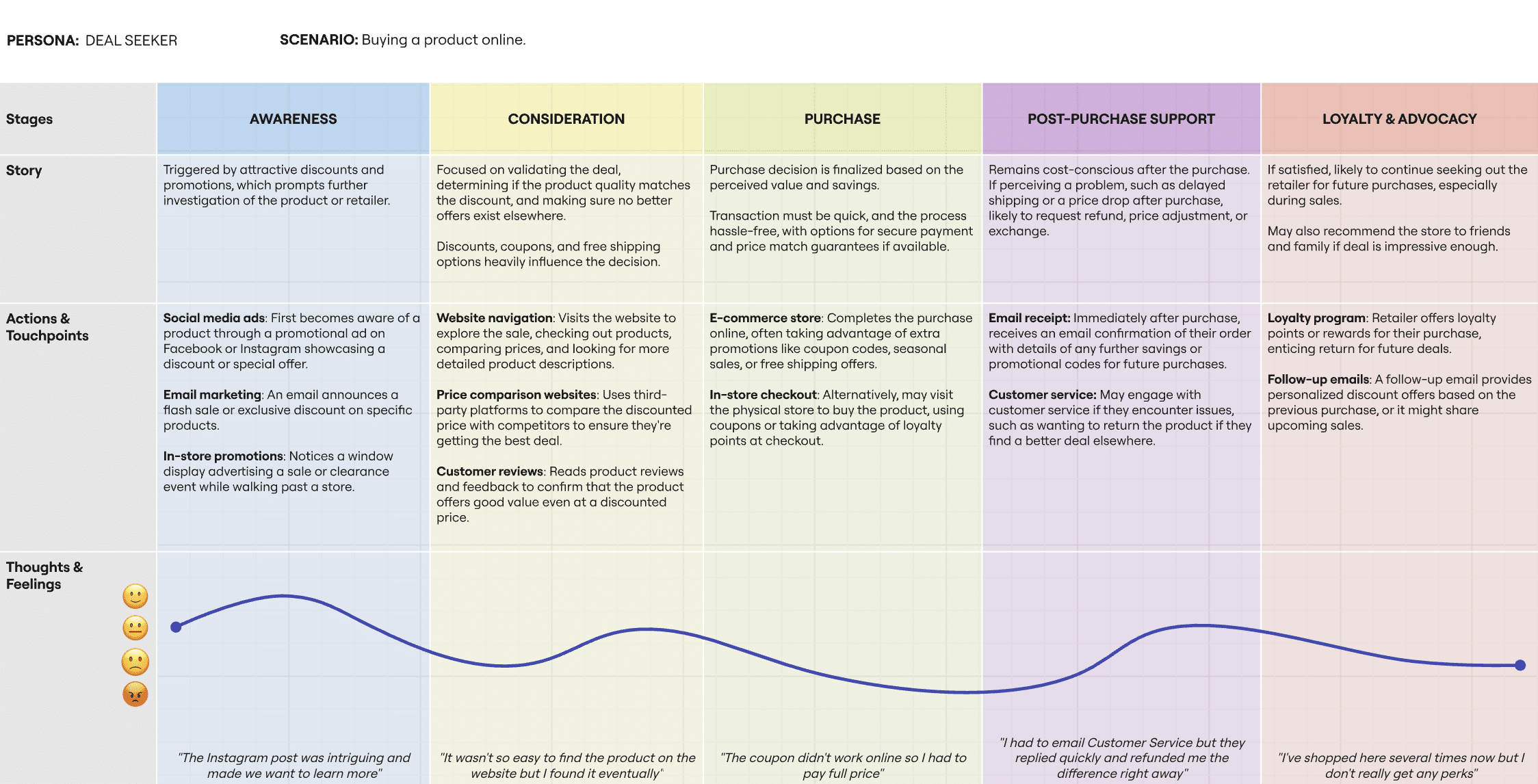
For this example, we used Miro to create a custom map. However, you can use plenty of tools to create your map, including design-focused ones like Adboe and Figma, or specialist tools such as TheyDo and Uxpressia.
How to improve the retail customer journey
Improving the retail customer journey starts with identifying customers’ pain points at different stages. This could involve streamlining the online shopping process, improving customer service, or creating more engaging follow-up communications. You should focus on making each touchpoint as seamless and satisfying as possible, whether the interaction happens online or in-store.
Additionally, offering personalized experiences can significantly improve customer satisfaction. Using data to anticipate customer needs and preferences, you can tailor your marketing efforts, product recommendations, and customer service to meet individual expectations.
Gathering data on the retail customer journey
Collecting and analyzing data is important for understanding the retail customer journey. You can gather data through various methods, including customer feedback platforms (like TruRating), web and social media analytics, and in-store observations. By combining these data sources with your commercial metrics, you can build a picture of the customer experience, identifying both successful touchpoints and areas needing improvement.
This data-driven approach allows you to make informed decisions about how to optimize the retail customer journey. For example, if data reveal that customers frequently drop off during the payment process, you might consider simplifying the checkout or offering more payment options.
Why are reviews helpful in the retail customer journey?
Retail is becoming increasingly complex, with customers interacting with brands across various channels, including physical stores, online platforms, apps, and social media. Understanding the retail customer journey is essential for delivering a seamless experience that meets and exceeds customer expectations. By mapping out the customer journey, you can identify key touchpoints, uncover pain points, and gather valuable insights into customer behaviors and emotions. However, the real challenge is in collecting and acting on this information within an omnichannel framework.
This is where TruRating makes a transformative difference. TruRating’s omnichannel feedback platform enables retailers to gather real-time feedback at every touchpoint—whether during in-store checkout, on an e-commerce website, through mobile apps, or even via email and SMS. This comprehensive approach ensures that no moment in the customer journey is overlooked, providing a clear and accurate picture of customer sentiment throughout their experience. With a continuous feedback loop, you can measure satisfaction levels, identify pain points, and uncover opportunities for improvement quickly and effectively.
TruRating doesn’t just provide feedback; it offers a powerful tool for retailers to measure, analyze, and enhance the customer journey at every step. To learn more about our omnichannel feedback software, book a demo today.